Image: Project Syndicate
By Stephen Holmes
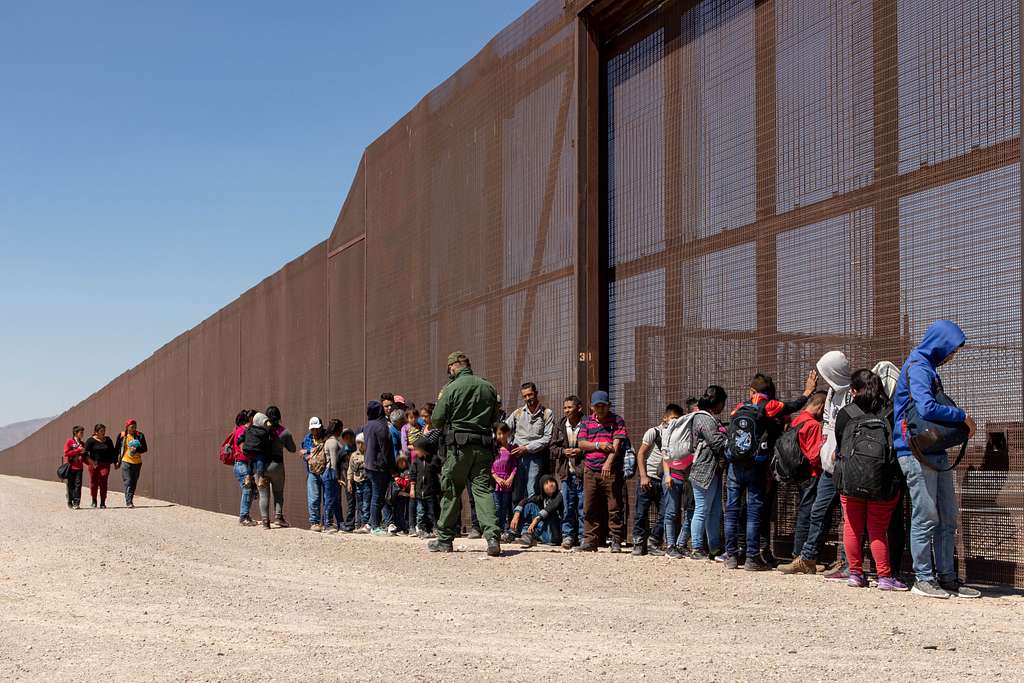
With Donald Trump laying claim to Greenland, Europeans have finally realized who they are dealing with. The US president is animated less by the prospect of deal-making than by the need for domination, less by the spirit of exchange than by the perverse pleasure of belittling others and exalting himself.
By threatening to seize Greenland by force, US President Donald Trump has exposed the childlike illusions of his European admirers. Having spent years cultivating their bromances with him, the continent’s right-wing populists – the United Kingdom’s Nigel Farage, Jordan Bardella in France, Alice Weidel in Germany, Italy’s Matteo Salvini, Robert Fico in Slovakia, Hungary’s Viktor Orbán, and Mateusz Morawiecki in Poland – imagined themselves fellow travelers in a revolt against liberal internationalism. Now their idol and patron has been threatening to swallow whole or in part (if the supposed “deal” he has announced comes about) the sovereign territory of a European ally.